
The healthcare industry is a dynamic and ever-evolving sector that plays a crucial role in society. The healthcare industry encompasses many services, including hospitals, clinics, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, health insurance and more. It is a vast and complex ecosystem that serves the needs of individuals, communities and populations.
Key Challenges in the Healthcare Industry:
- Rising Costs: Healthcare costs continue to soar, posing a significant challenge for providers and patients. Factors such as advanced medical technologies, increasing drug prices and the ageing population contribute to the cost burden.
- Access to Care: Disparities in access to healthcare services persist globally. Many individuals face barriers such as financial constraints, geographic location and a lack of healthcare infrastructure, resulting in unequal access to quality care.
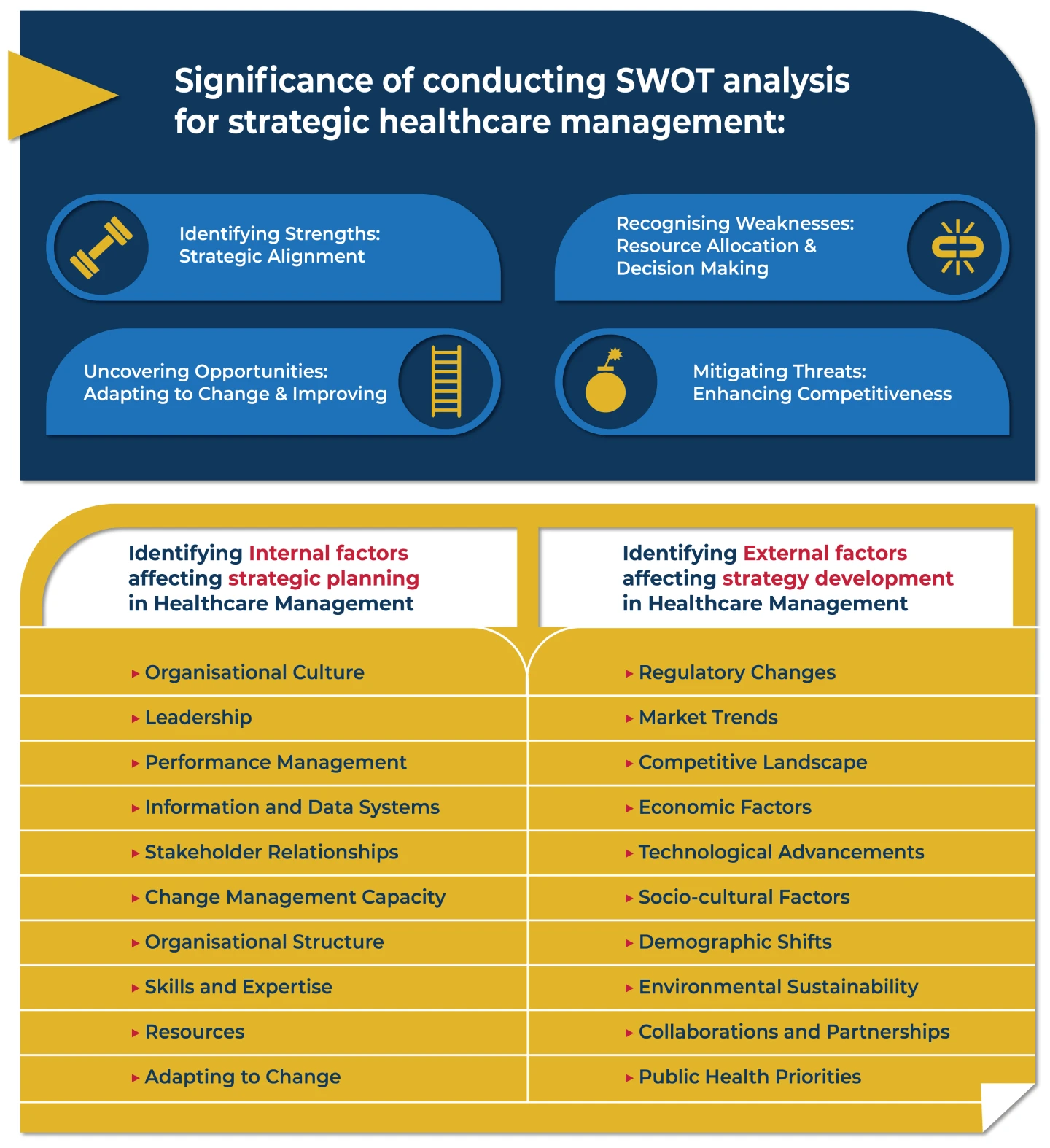
- Regulatory Environment: Healthcare organisations must navigate a complex regulatory landscape with evolving laws, policies and compliance requirements. Adapting to regulatory changes while maintaining operational efficiency is a significant challenge.
- Technological Advancements: Rapid advancements in healthcare technologies, such as telemedicine, electronic health records (EHRs) and artificial intelligence, introduce opportunities and challenges. Organisations must stay updated and invest wisely in technology to enhance patient care and optimise operations.
- Demographic Shifts: Changing demographics, including an ageing population and the rise of chronic diseases, pose unique challenges for healthcare organisations. Providing specialised care for specific age groups and managing complex healthcare needs require strategic planning and effective resource allocation.
Trends Impacting Strategic Planning:
- Population Health Management: The shift from a fee-for-service model to a value-based care approach emphasises proactive population health management. Healthcare organisations focus on preventive care, managing chronic conditions and improving overall health outcomes.
- Consumer-Centric Care: Patients are increasingly participating in their healthcare decisions. This trend requires healthcare organisations to adopt patient-centred approaches, enhance engagement and personalise care delivery.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The availability of vast healthcare data allows organisations to leverage analytics and data-driven insights. Strategic planning must incorporate robust data analysis to drive informed decision-making and improve outcomes.
- Collaborative Care Models: Collaborative care models, such as accountable care organisations (ACOs) and care coordination initiatives, are gaining prominence. Strategic planning should consider partnerships, care networks and interdisciplinary collaboration to improve care coordination and patient outcomes.
- Emphasis on Quality and Patient Safety: In an era of transparency and accountability, healthcare organisations must prioritise quality and patient safety. Developing strategies focusing on continuous quality improvement, patient safety protocols and evidence-based practices is crucial.
The Need for Adaptability:
Healthcare organisations operate in a constantly evolving environment. They must adapt to changes driven by technological advancements, shifting demographics, regulatory updates and emerging healthcare trends. Strategic planning is essential to navigate these changes successfully and seise new opportunities. Organisations that fail to adapt will risk falling behind and compromising their competitiveness, patient satisfaction and financial sustainability.
Healthcare diploma programme & the Fundamentals of Strategic Planning in Healthcare
Strategic planning is a critical process that guides healthcare management in setting a clear direction, making informed decisions and allocating resources effectively.
Diploma courses in healthcare management cover this key area, providing a clear understanding of the systematic processes that underline an organisation's long-term goals and the roadmap to achieving them. Strategic planning encompasses a range of activities, including assessing the internal and external environment, setting objectives, formulating strategies, implementing action plans and evaluating outcomes. The aim is to align the organisation's resources, capabilities and actions to fulfil its mission and achieve sustainable success.
Critical Components of a Strategic Plan:
- Mission: The statement represents the organisation's purpose, why it exists and its fundamental role in the healthcare industry. It outlines the organisation's core values, target population and the benefits it aims to provide.
- Vision: This outlines the desired future state or outcome that the organisation strives to achieve. It is an aspirational guidepost, inspiring and motivating stakeholders by painting a compelling picture of the organisation's future impact.
- Values: Values represent the principles and beliefs guiding the organisation's actions and decision-making. They serve as a moral compass and shape the organisation's culture, ethics and stakeholder interactions.
- Goals: Goals are broad, overarching statements that outline what the organisation intends to achieve within a specific timeframe. They are aligned with the mission and vision and provide a strategic direction for the organisation's efforts.
- Objectives: Objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound (SMART) targets that support achieving goals. They provide clear milestones and actionable steps to reach desired outcomes.
Importance of Stakeholder Analysis and Engagement:
Stakeholders (individuals/groups) are vested in the organisation's actions and outcomes. Effective stakeholder analysis and engagement are crucial in strategic planning for the following reasons:
- Identifying Key Players: Stakeholder analysis helps identify key individuals and groups who can influence or are affected by the organisation's strategies and decisions. This includes patients, employees, healthcare providers, regulatory bodies, insurers and community members.
- Understanding Needs and Expectations: Engaging stakeholders enables organisations to understand their needs, expectations and concerns. This understanding helps shape the strategic planning process and ensures that the organisation's strategies align with stakeholder interests.
- Building Support and Collaboration: Involving stakeholders in strategic planning fosters ownership, buy-in and commitment to the organisation's goals and strategies. It promotes collaboration, partnerships and shared accountability for successful implementation.
- Managing Resistance and Mitigating Risks: Stakeholder analysis helps identify potential sources of resistance, conflicts of interest, or risks that may hinder strategy implementation. Proactive engagement allows organisations to address concerns, build consensus and mitigate risks effectively.
By incorporating stakeholder analysis and engagement into strategic planning, healthcare organisations can ensure that their strategies are well-informed, responsive and inclusive. This holistic approach increases the likelihood of successful strategy implementation and fosters positive stakeholder relationships.
Learning to Set Strategic Goals & Objectives with healthcare diploma programme
Setting strategic goals that align with the organisation's mission and vision is a crucial step in strategic planning for healthcare management. Let's learn more about it:
Setting Strategic Goals::
- Review Mission and Vision: Revisit the organisation's mission and vision statements. These statements provide the overarching purpose and desired future state as a foundation for setting strategic goals.
- Identify Priority Areas: Identify critical areas or themes that align with the mission and vision and are essential for the organisation's success. For example, improving patient outcomes, expanding access to healthcare, enhancing operational efficiency, or promoting innovation.
- Consider Stakeholder Input: Seek input from stakeholders, including employees, patients and community members, to ensure their perspectives and needs are reflected in the strategic goals.
- Define Broad Goals: Formulate broad, high-level goals that encapsulate the desired outcomes the organisation aims to achieve. These goals should be specific to the organisation's unique circumstances and strategic priorities.
Importance of SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) Objectives:
SMART objectives provide a framework for setting clear, measurable and actionable goals. They help ensure that strategic plans are well-defined and provide a roadmap for implementation and evaluation. Here's what each component of SMART represents:
- Specific: Objectives should be clear, concise and specific, leaving no room for ambiguity or misinterpretation. They should clearly state what is to be accomplished.
Example: Increase patient satisfaction scores by 10% within the following year.
- Measurable: Objectives should include quantifiable measures to track progress and determine success. They provide a means to assess the achievement of the desired outcomes.
Example: Reduce patient wait times in the emergency department by 20% within six months.
- Achievable: Objectives should be realistic and attainable given the organisation's available resources, capabilities and constraints. They should stretch the organisation but still be within reach.
Example: Increase employee training and development programs by 15% within the budgetary constraints of the organisation.
- Relevant: Objectives should align with the overall strategic goals and be relevant to the specific context and priorities.
Developing and implementing Strategies learnt with diploma in healthcare
In healthcare management, strategic approaches shape the path to achieving organisational goals. Here, we discuss key strategic approaches, goal alignment and the importance of innovation and adaptability.
- Strategic Approaches:
Cost Leadership: Delivering healthcare services at a lower cost than competitors.
Differentiation: Offering unique and distinctive healthcare services.
Focus/Niche Strategy: Targeting a specific patient population or specialised services.
- Aligning Strategies with Goals:
Clearly define goals and objectives and choose an approach that aligns with them.
Conduct internal and external analyses to understand capabilities and market conditions.
Consider stakeholder perspectives for their support and satisfaction.
Create an implementation plan and monitor progress regularly.
- Importance of Innovation and Adaptability:
Innovation drives improvements in patient care, operational efficiency and outcomes.
Adaptability enables organisations to respond effectively to changes and challenges.
Foster a culture of continuous learning and collaboration.
Seek partnerships for knowledge-sharing and joint innovation.
By aligning strategies, embracing innovation and being adaptable, healthcare organisations position themselves for long-term success in an evolving industry.
Transform and Grow with GBS Dubai’s diploma in healthcare

If you are looking for a transformative course to uplift your career in the healthcare sector, GBS Dubai offers a wide range of industry-focused courses designed to fit around a student’s busy schedule. At GBS Dubai, students embark on their transformational and life-changing journey through education. Students get unique access to learning, regardless of their background.
GBS Dubai aspires to deliver the finest educational experience for students. The HND in Healthcare Practices (Healthcare Management) offered by GBS Dubai is a two-year course offered by GBS Dubai. Out of all the healthcare management courses in Dubai, this diploma in healthcare aims to develop adaptable professionals who can thrive in the fast-growing healthcare sector.
Healthcare management courses in Dubai enhance academic skills for better prospects in higher education.
Why Choose a Diploma in Healthcare from GBS Dubai:
- GBS's healthcare management course in Dubai was designed by Pearson, making it recognisable globally.
- The course equips students with valuable skills and industry knowledge for success in the global health and social care environment.
- GBS Dubai provides a productive learning environment that simulates a workplace, enhancing students' skills and employability.
- Studying the HND healthcare practice course in Dubai opens doors to employment and further education opportunities in the UAE and internationally.
Career Opportunities::
- Healthcare support and assistant roles in various settings.
- Nursing assistant/auxiliary roles.
- Care navigation, planning and assessment roles.
- Public health, health promotion and non-clinical healthcare supervisory or lower management roles.
- Opportunities for progression to higher education qualifications in nursing, public health, healthcare administration, or related areas.
Roles After Healthcare Diploma Programme Completion:
- Operations Manager
- Customer Service Manager
- Medical Administrator
- Medical Records Administrator
- Non-clinical managerial, coordinator and supervisory roles in healthcare administration, operations and support services.
Benefits of the healthcare diploma programme in Dubai:
- Gain insight into diverse roles within the healthcare sector.
- Develop skills in collaboration and cross-cultural understanding.
- Opportunities to enter the healthcare workforce or progress to higher education.
If you are looking for an HND in Healthcare Practice course that provides a solid foundation for students and beginners. Seek a rewarding career in the healthcare sector with this healthcare diploma programme. It equips students with the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in various healthcare roles while offering pathways for further education and professional growth.




